The more forests we lose every year, the more we recognize their importance in different industries and daily routines. Awakened by the threat of climate change and alarming forest loss, modern businesses that are in any way connected to forestry start recognizing the need for related mitigation activities. The umbrella term for them is forest restoration — a crucial initiative aimed at reviving degraded ecosystems, enhancing biodiversity, and increasing resilience to climate change. The process involves replanting native trees to restore soil health and revitalize habitats for wildlife. Luckily, there is an innovative technology to help with all this.
This article focuses on satellite data analytics — an invaluable tool in restoration efforts. By offering a comprehensive view of forest conditions and changes, free high-resolution satellite imagery allows for more precise and effective restoration strategies, paving the way for a healthier and more resilient planet. But before we jump into more details, let’s discuss why it’s even important.
Why Care About Forest Ecosystems
It’s common knowledge that trees are pillars holding the Earth’s environmental balance by acting as carbon sinks and absorbing vast amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. But, as we’ve mentioned in the beginning, their role stretches beyond that. Forests also regulate water cycles, maintain soil health, and provide habitat for a multitude of species. And it works both ways. For example, healthy soil supports tree growth — tree roots support soil health. However, deforestation and forest degradation, driven by logging, agriculture, urban expansion, and aridification have led to significant losses of forest cover globally. Restoring these forest is essential to sustaining ecosystem services and ensuring ecological stability.
Satellite Data and Analytics in Forest Monitoring
There is no doubt that technology has become a powerful ally in the realm of forest conservation and restoration. One of the most transformative advancements is the use of satellite data and analytics in forest monitoring. With the ability to get access to high-resolution satellite images, scientists and environmentalists can now observe and analyze vast expanses of forest in unprecedented detail. Such an approach not only enhances our understanding of forest dynamics but also provides critical insights for effective management and conservation strategies. By harnessing the power of satellite tech, we can better protect our precious green landscapes and ensure their health and sustainability for future generations. Let’s see how it works for exact purposes.
Deforestation Detection
By leveraging advanced satellite technologies, we can monitor vast forested areas with remarkable precision and timeliness. This method allows for the detection of deforestation events in near real-time, identifying even subtle changes in forest cover that might go unnoticed be it any other way of observation.
High-resolution satellite images provide detailed visual data, enabling researchers to pinpoint the exact locations and extent of forest loss.
This kind of knowledge is vital for policymakers and conservationists, enabling them to respond swiftly and effectively to illegal logging activities, desertification, and other threats to forest ecosystems.
Monitoring Reforestation Projects
For the reforestation to be effective, there has to be proper forest management: one that caters to specific goals, such as recovery from deforestation, harvesting, or wildfires. The choice of trees varies with these goals: some species excel in carbon absorption, while others grow quickly.
Restoring ecosystems depends on planting diverse species. Monoculture forests are vulnerable to disease, whereas polyculture forests enhance biodiversity and resilience. Techniques like clearcuts or prescribed fires can accelerate natural restoration.
Remote sensing simplifies reforestation management, especially in inaccessible areas. High-resolution satellite imagery provides early insights into progress and detects problems promptly. Vegetation indices help foresters identify and address unhealthy areas, ensuring successful reforestation.
Assessing Forest Health
A powerful tool here is utilizing vegetation indices, such as the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI). This way researchers can evaluate the vitality of forests with remarkable accuracy. NDVI values, derived from high-quality satellite images, depict the difference between visible and near-infrared light reflected by vegetation, providing insights into plant health, biomass, and productivity.
These indices highlight areas of vegetation stress or disease, allowing for early detection of issues that could escalate into significant problems. Satellite imagery enables continuous monitoring over large areas, ensuring that even remote or inaccessible forests are included in health assessments. This technology equips environmentalists and policymakers with the data needed to make informed decisions, implement timely interventions, and develop strategies for sustainable forest management.
Carbon Sequestration Measurement
By utilizing satellite data, experts can accurately estimate the carbon content stored in forests through detailed measurements of tree biomass and growth rates. This advanced technology enables them to quantify the impact of restoration projects on mitigating climate change, providing valuable insights into how effectively these efforts are reducing atmospheric carbon levels.
Through such precise monitoring, we can better understand and enhance the role of forests in our global climate strategy.
Planning And Tracking Afforestation
To ensure successful afforestation and sustainable forest plantations, precise monitoring is key. This is achieved by using data from various satellites like Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2, and the power of machine learning to compile bi-weekly forest cover data.
Choosing the right tree species is also crucial. Analyzing local forest inventories helps select species that thrive, ensuring a positive impact on the ecosystem. Historical satellite imagery can help track regrowth, and combined with spatial analysis, provides a comprehensive view of forest dynamics. This aids in managing tree loss and replanting efforts quite effectively.
Benefits of Remote Sensing
Remote sensing offers numerous benefits for forest monitoring. It provides an enhanced spatial representation of the monitored area and covers large geographical regions systematically. Non-intrusive and systematic data collection methods ensure minimal disruption to the environment. Increased data frequency allows for more accurate observations, enabling rapid decision-making. Additionally, remote sensing can acquire information in challenging or inaccessible areas, potentially reducing the costs of monitoring programs.
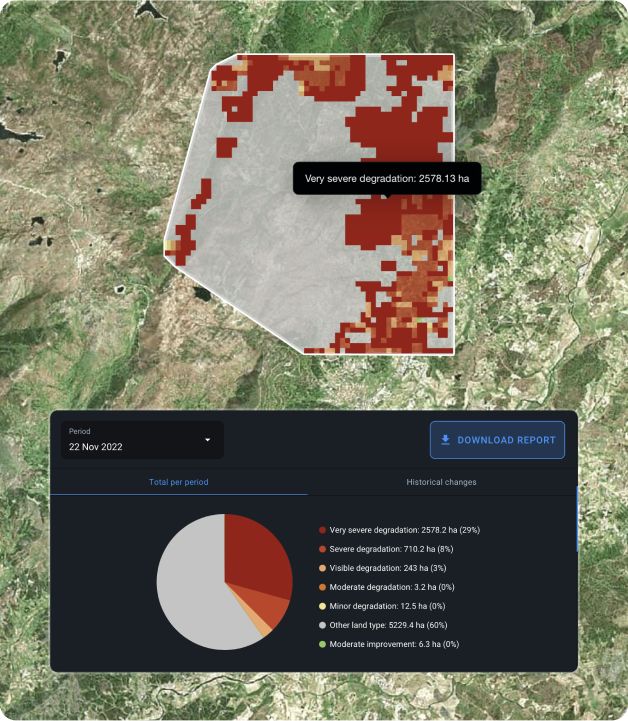
At Green Initiative, we utilize high-resolution satellite data for various applications. Over longer periods (e.g. above 3 years) we monitor the abundance of vegetation in our restoration sites by measuring the change in NDVI over time. The results of these measurements allow us to corroborate the observations made by our local restoration partners when monitoring the restoration sites, adding a layer of credibility. Additionally, we apply land use and arboreal cover satellite data to identify key areas for restoration.
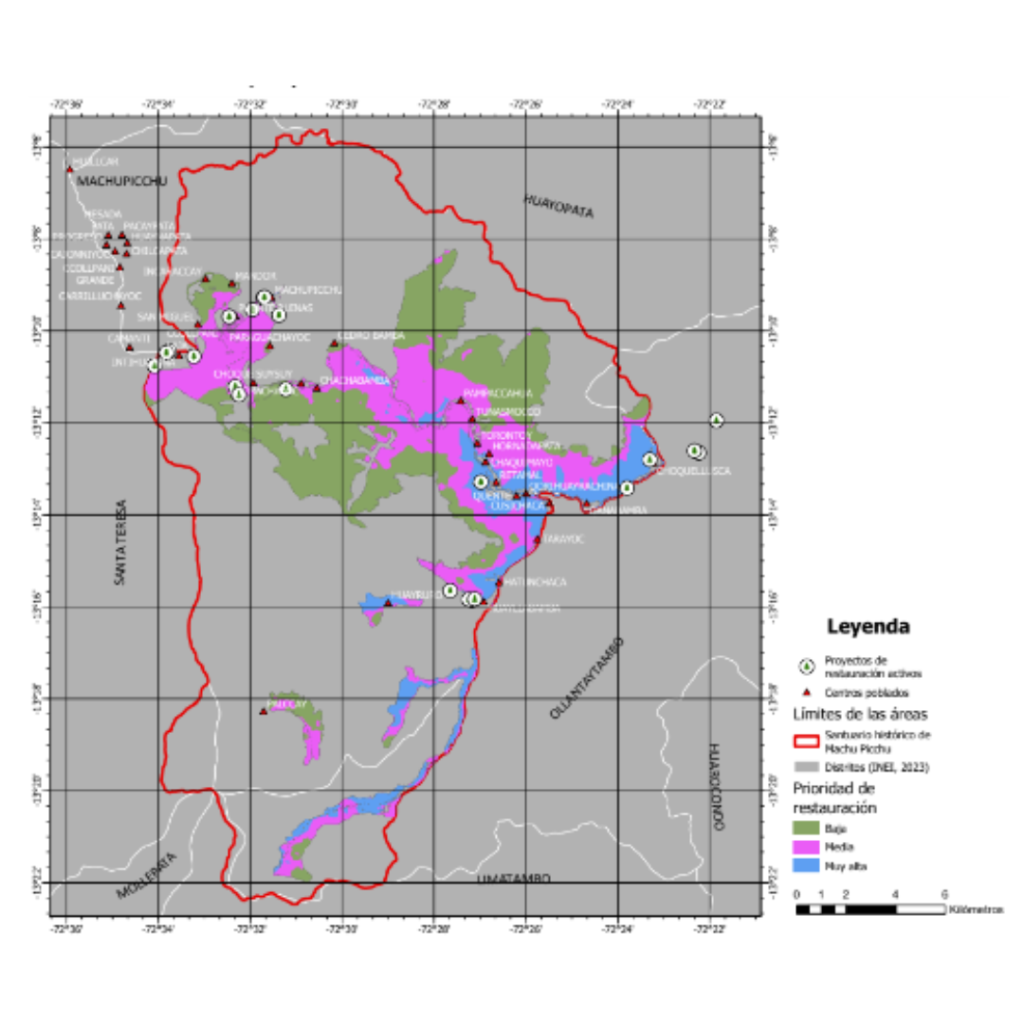
For example, we have identified priority areas (low, medium, and high priority) within the recuperation zone of the Machu Picchu sanctuary that are particularly vulnerable to continued forest and vegetation loss due to elevated surface temperatures and sparsity of tree cover, both of which hinder seed dispersal and forest resilience to climate change. These applications are at the forefront of Green Initiative’s methodologies and contribute to the efficient management of restoration efforts.
Challenges and Future Directions
Using satellite data for forest restoration has its challenges as high-resolution Earth images can be costly as they require expertise to analyze or, in other cases, ground truthing. Additionally, cloud cover and atmospheric conditions can hinder data collection.
However, advancements in technology are making these tools more accessible and affordable. Future innovations, such as hyperspectral imaging and the increased use of low-cost drones, promise to provide even more detailed insights into forest ecosystems. These developments will enhance the effectiveness of forest management and restoration efforts.
This article was written by Kateryna Sergieieva from EOS Data Analytics in collaboration with Marc Tristant from the Green Initiative team.
Kateryna Sergieieva has a Ph.D. in information technologies and 15 years of experience in remote sensing. She is a scientist responsible for developing technologies for satellite monitoring and surface feature change detection. Kateryna is an author of over 60 scientific publications.
Contact us for expert advice on Ecosystem Restoration initiatives and becoming a nature-positive business organization.

